Introduction
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are essential to diagnostics and therapeutic research, serving as rich sources of biomarkers and key mediators of intercellular communication. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is widely used for isolating EVs due to its simplicity, reproducibility, and gentle purification conditions. In our previous white paper, “Why is SEC becoming the most widely used EV isolation technique?”, we detailed how Sepharose CL-4B provides suitable pore sizes for efficient EV isolation from plasma or serum samples. Here, we examine the limitations of large and small pore-size resins for the separation of lipoproteins from EVs and introduce Everest Biolabs’ Apex MM columns that overcome these limitations. Everest Biolab’s Apex MM column leverages SEC and multi-mode resins to significantly enhance the purity of EV isolate against lipoproteins while maintaining high yield and minimal size bias against small EVs.
Challenges in Lipoprotein Co-elution with EV Isolation
EVs typically range from 30 to 200 nm (Gurung, S et al., 2021), overlapping in size with various lipoproteins: HDL (~8–13 nm), LDL (~18–25 nm), and VLDL (~30–80 nm) (Liangsupree et al., 2020). This overlap presents a considerable challenge in EV isolation, as traditional SEC columns can co-isolate these lipoproteins, compromising sample purity. Studies indicate that smaller pore resins (like Sepharose CL-4B with pore size of 35nm) tend to increase co-elution of lipoproteins due to the restricted separation range, while larger pore resins (such as Sepharose CL-2B with pore size of 70 nm) may improve purity but reduce EV yield (Guo et al., 2021; Liangsupree et al., 2020).
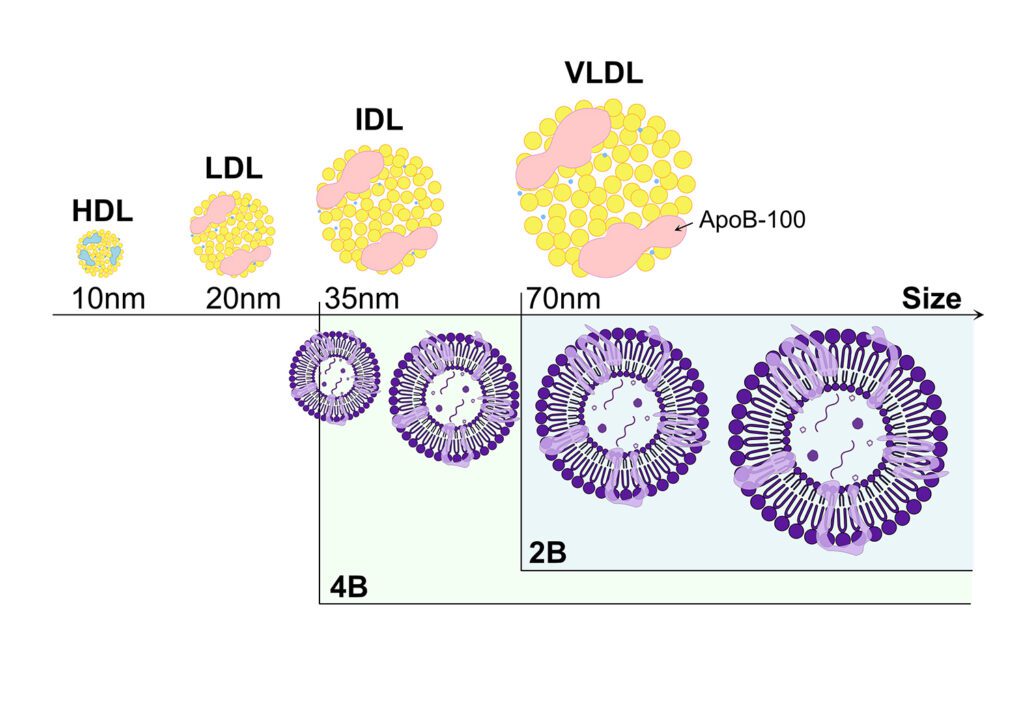
Figure 1: Lipoprotein depletion using SEC columns. Major plasma lipoproteins and their size overlap with EVs, relative to SEC resins with 35 nm (4B) and 70 nm (2B) cutoffs. The 2B resin more effectively separates EVs from lipoproteins, but at the cost of reduced EV yield and enrichment for larger EVs.
Introducing Apex Multi-mode columns:
Everest Biolabs has developed Apex MM columns by combining size exclusion chromatography (SEC) resin with a small pore size and a multi-mode (MM) resin that uses hydrophobic interaction and ion-exchange to selectively bind and remove lipoproteins and other soluble contaminants, significantly enhancing EV purity. Figure 2 presents data from plasma EVs isolated using the Apex MM column. While EV yield from Apex MM is lower than that of the Apex 4B column, it is higher than the yield from the competitor qEV70 column. Importantly, Apex MM columns achieve the highest purity, as measured by reduced levels of major protein contaminants, including apolipoproteins (ApoA1 and ApoB-100) and human serum albumin (HSA). Apex MM columns are particularly advantageous for unbiased downstream analyses such as proteomics, whereas Apex 4B columns are better suited for targeted assays like ELISAs or Western blots (Table 1).
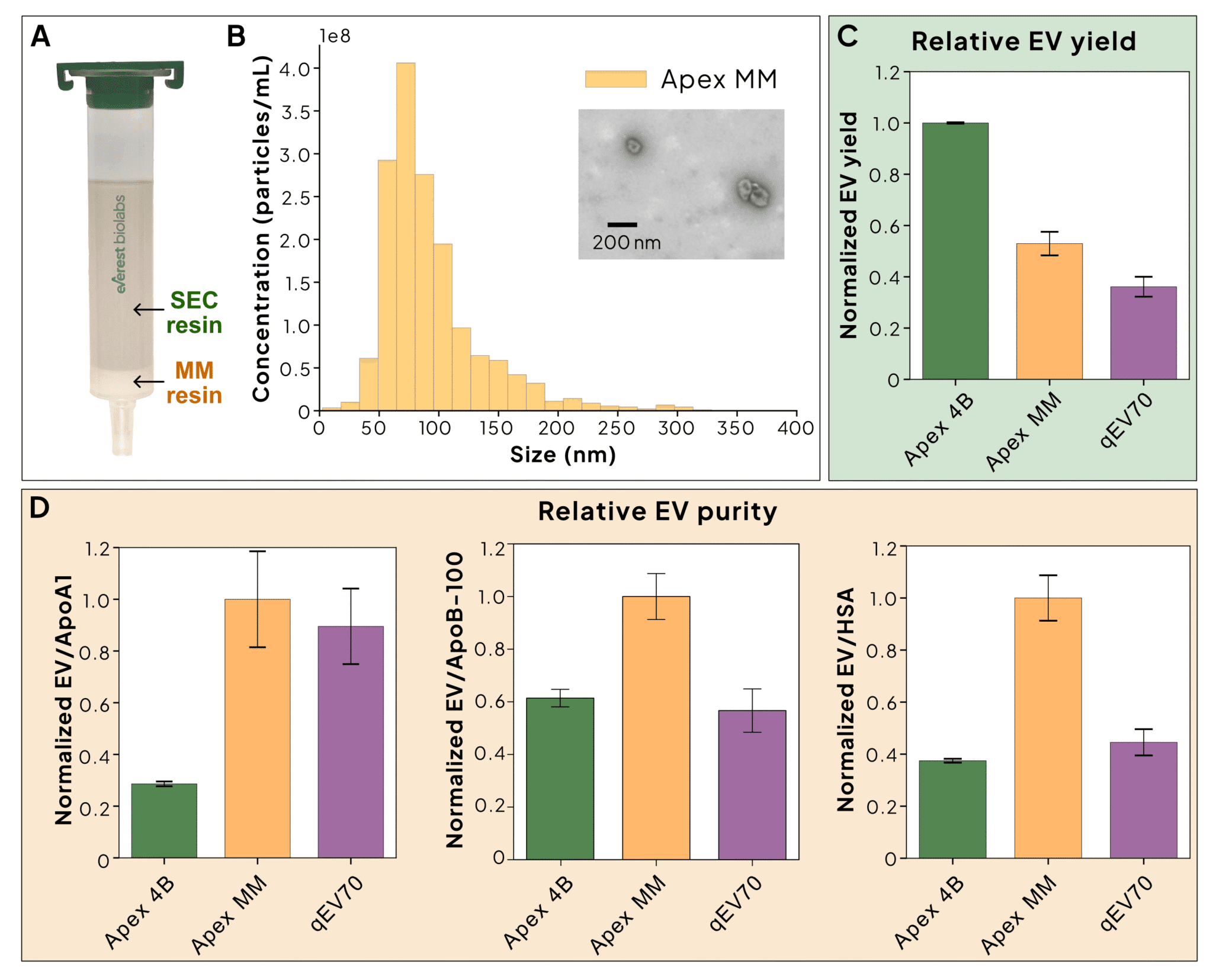
Figure 2: Performance of Apex MM columns.
A. Structure of a multi-mode (MM) column with a secondary resin below the SEC layer to enhance lipoprotein and secreted proteins depletion. B. Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of pooled EV fractions isolated from plasma using the Apex MM column, with a representative TEM image showing typical EV morphology. C. Plasma samples were processed using Apex 4B, Apex MM, and qEV70 columns. EV levels were quantified using the Atlas EV ELISA and normalized to the highest measured value. D. Concentrations of ApoA1, ApoB-100, and human serum albumin (HSA) were measured by ELISA. EV purity was calculated by dividing EV levels by each contaminant level, and values were normalized to the highest column-specific ratio.
Table 1: Comparative Analysis of SEC Columns for isolating EVs from Plasma/Serum:
| Column Name | Resin Composition | Size cutoff | Secreted protein depletion | Lipoprotein depletion | EV yield | Recommended Applications | Soluble Proteins Isolation |
| Apex MM | cross-linked agarose | < 50 nm | Very High | Very High | Moderate | Untargeted: Mass spec RNA seq NTA Flow Cytometry | No – soluble proteins are trapped in the MM resin |
| Apex 4B | 4% cross-linked agarose | ~35 nm | High | Moderate | High | Targeted protein assays: (ELISA/Western) | Yes |
| qEV70 | N/A (proprietary) | ~70 nm | High | Very high | Low | No – Small EVs will elute with soluble proteins |
Conclusion
Everest Biolabs’ Apex MM columns overcome limitations inherent in traditional SEC columns by effectively managing the trade-off between purity and yield. By providing superior EV purity, maintaining optimal yield without introducing size biases, and preserving EV functionality, Apex MM columns significantly enhance biomarker discovery and therapeutic research applications. The Apex MM columns are compatible with the Ascent instrument, allowing for the simultaneous running of 8 samples automatically.
References:
- Gurung, S., Perocheau, D., Touramanidou, L. et al. (2021). The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun Signal 19, 47.
- Liangsupree, T., Multia, E., & Riekkola, M.-L. (2020). Modern isolation and separation techniques for extracellular vesicles. Journal of Chromatography A, 1636, 461773.
- Dmitry Ter-Ovanesyan, Tal Gilboa et al. (2023). Improved isolation of extracellular vesicles by removal of both free proteins and lipoproteins. eLife 12:e86394.
- Guo, S., et al. (2021). Purification of exosomes – a comparison of methods and market analysis. DiVA Portal.